What are the Stages of quality system development? How is quality the basis for the sustainable success of organizations?
- Posted by:
- Category: Uncategorized

Do you know how Japan went from a poor country with no resources, a victim of a nuclear bomb that lost 75,000 people, to the most powerful economic and industrial country in the world?
Quality is the secret behind Japan’s transformation and survival until now. What is quality, the Stages of quality system developmentt, and how it is the reason for the lasting success of the business is what we discuss in the article, so let’s go.
Why are there so many quality system concepts?
The quality system concepts were initially the concept of quality at the right price until the prevailing concept now among organizations is to anticipate the needs of the customer and achieve complete satisfaction through the quality of the product that is offered to the customer.
This means that organizations are interested in providing products or services that meet the needs and requirements of customers and are linked to specific specifications. The definitions of quality have varied according to these definitions, as quality has been defined by experts such as:
- Armand Feichbaum 1956, who defined it as (total customer satisfaction), believes that quality does not only mean that the product is free of defects, but more importantly that it is useful and satisfactory to the customer. If the product works well, and achieves the purpose that the customer wants from it in the way he expects, this is a good product.
- As defined by Crosby (1979), quality is (conformity to requirements). In other words, the product or service is executed and delivered exactly as required and agreed upon, without errors or excesses, which minimizes waste and costs. For example, if an organization sets precise specifications for a product (e.g. size, color, function…), what is required is strict adherence to these specifications. Therefore, quality does not mean “the best”, but rather “accurate and conforming to what is expected”.
- In 1989, Joseph Juran defined quality as (the accuracy of use as perceived by the beneficiary) or suitability for use. This means that the product or service performs its required function as expected by the user. Juran’s philosophy is that quality is not only the absence of defects, but that the product performs its purpose effectively.
In addition to linking quality to practical customer satisfaction and not just theoretical specifications. Juran explains that quality should be designed into the product from the beginning, not discovered after production.
- William Deming defined it in 1986 as (an expected degree of consistency and reliability that suits the market at a low cost), meaning that the product works with the same efficiency every time, and fulfills what the customer requires now, and even his potential future needs. He was one of the first to link quality to long-term customer satisfaction
Despite the different concepts of quality, they were all unified by a phrase that clarifies the current concept of quality, which is (satisfying the desires of the customer / beneficiary at the present time and in the future)
Why has quality become more important than ever?
Due to the increasing expectations of customers and the variety of options available to them, organizations are required to provide products and services that not only meet the requirements but also exceed expectations. The reasons for the increasing importance of quality in the modern era can be summarized as follows:
- Rising customer awareness and expectations
- Digitalization and market transparency
- Global competition
- Increasing complexity in supply chains
- Need for sustainability and social responsibility
- Rapid development of technology
 What is The Importance of Quality Management System
What is The Importance of Quality Management System
The Importance of Quality Management System (QMS) is one of the main pillars on which successful organizations are built, whether in the industrial or service sector. The role of a QMS is not limited to improving the quality of a product or service, but rather extends to controlling processes, achieving efficiency and innovation, and increasing customer satisfaction. The following aspects highlight the importance of a quality management system
- Standardizing processes and reducing variability
By documenting procedures and applying standards, the quality system helps to standardize the way of working and reduce variability between production units or service delivery, which promotes consistency in results.
- Increase customer satisfaction
Quality management helps to accurately meet customer expectations, improving the customer experience and building long-term relationships based on trust and loyalty
- Reduce waste and increase efficiency
Thanks to the analysis and audit tools provided by the system, the organization is able to detect weaknesses in processes and reduce waste, whether in time, resources or costs.
- Improving competitiveness
Implementing an effective quality system contributes to raising the reputation of the organization and increasing its ability to compete locally and internationally, especially if it holds recognized certificates such as ISO 9001.
- Making data-driven decisions
A quality system helps to systematically collect and analyze data, enabling management to make accurate and thoughtful decisions based on actual performance and not assumptions.
- Fostering a culture of continuous development and improvement
The QMS adopts the philosophy of Continuous Improvement through periodic evaluation, dynamic response to changes, and motivating internal teams to self-development.
- Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements
A quality system helps organizations comply with applicable legislation and industry standards, which protects them from legal violations and operational risks.
So it is clear that the Quality Management System is not just documents or procedures, but a comprehensive framework that drives the organization towards operational excellence and market leadership.
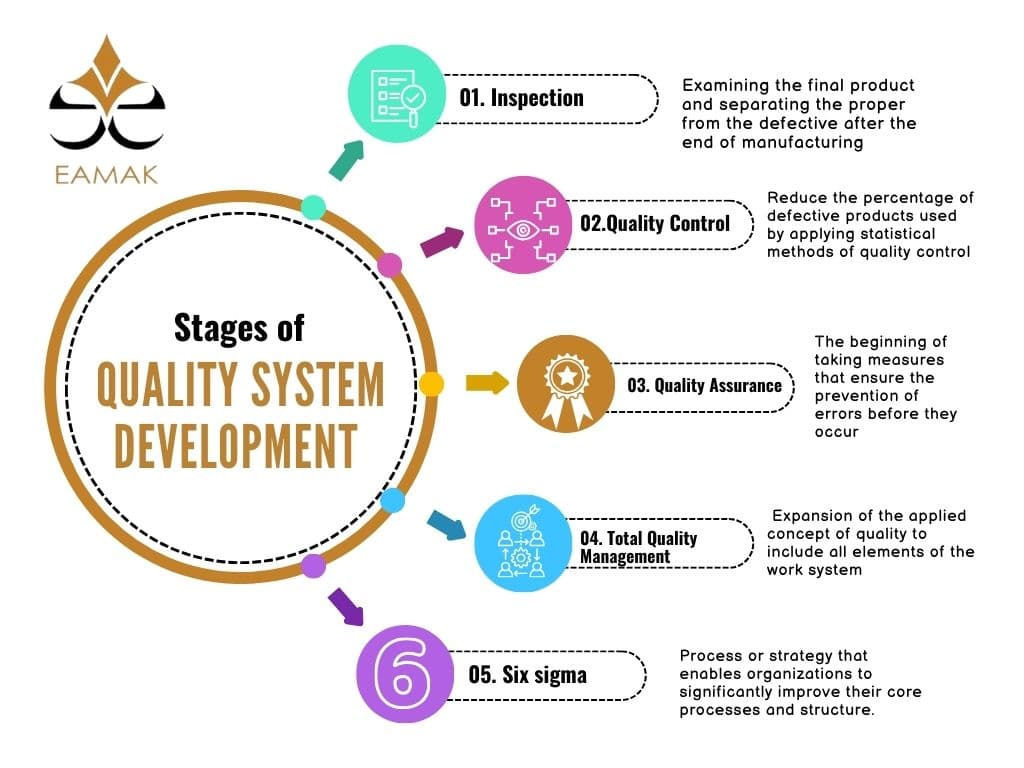
The Five Stages of quality system development
The stages of quality system development reflect the evolution of administrative and technical thinking within organizations, from simple manual practices to complex and integrated systems in the digital age. Each of these stages came in response to specific challenges and changing needs in the industrial and commercial environment. The evolution of the quality system comes in five stages
- The first stage: INSPECTION
From 1920 to 1940 at the beginning of the industrial revolution, this stage aimed at the final inspection, which means examining the final product and ensuring that it conforms to the specifications through manual inspection by a worker and separating the proper from the defective after the end of manufacturing. At that stage, there were no mechanisms to prevent the error but only to detect it and ensure that defective products do not reach the consumer.
- Second Stage: QUALITY CONTROL
From 1940 AD until the late 1960s, this stage aimed to reduce the percentage of defective products used by applying statistical methods of quality control, and the focus at that stage remained on detecting and minimizing the percentage of defects in the final product, not preventing them.
- Third stage: QUALITY ASSURANCE from 1970 to 1985
This stage is the beginning of taking measures that ensure the prevention of errors before they occur and maintain the levels achieved and ensure their stability, and this is done by monitoring the production process to ensure that the products come out without defects every time. This is done by monitoring the elements of the production process, including:
- Man
A skilled and trained worker helps to produce products that conform to specifications and do not have errors because he is not the only element in the production process, while an unqualified worker guarantees a product that does not conform to specifications.
- Equipment
- Machine
- Materials
- Work Methods
- Measurement Tools
- Work Environment
Standards for achieving quality assurance
To achieve quality assurance, there are a set of important international standards (ISO) that will help organizations reach the best level of quality and efficiency. Organizations that have applied these standards obtain an ISO certificate, which varies according to the company’s field of work, the most famous of which are:
- ISO 9001: It is concerned with applying quality standards in all processes and activities to increase the organization’s ability to provide high-quality services and products
- ISO 14001: It is concerned with applying environmental compliance standards and ensuring that the organization does not cause any serious damage to the environment.
- ISO 45001: Concerned with occupational safety and health, that is, concerned with the safety of facilities and control of risks that threaten the security of workers and how to behave properly in the event of an emergency.
Obtaining an ISO certificate in your organization is of great importance:
- Customer confidence
- Raising the quality of products and services
- Increased competitiveness
- Improving operational efficiency
- Fourth stage: Total Quality Management
The goal at this stage became the comprehensive and continuous development of quality systems and teamwork, in addition to the expansion of the applied concept of quality to include all elements of the work system to minimize errors in all production and administrative processes.
One of the most prominent tools of this stage is the use and development of quality management information systems (from 1986 to 1979).
TQM is characterized by several features, for example
- Focusing on customer satisfaction as a priority.
- Continuous improvement in all processes.
- Involving all employees in quality responsibility.
- The use of analysis tools such as causal analysis, process maps, and quality teams.
- The fifth stage: (Six sigma)
It is the latest advanced stage of quality systems and is considered a qualitative shift in how to deal with quality on a global level. It first appeared at Motorola in the mid-1980s and was then widely adopted by General Electric to make a real shift in the concepts of operational efficiency. Six sigma can be defined as a process or strategy that enables organizations to significantly improve their core processes and structure.
This is done by designing and controlling daily business activities so that waste and consumption of resources (time – mental energy – physical energy) are minimized while at the same time meeting the needs of the customer and achieving customer satisfaction. The Six Sigma principle indicates that the organization provides services or goods almost free of defects because the defect rate in Six Sigma is 3.4 defects per million opportunities, which means that the efficiency and effectiveness of operations is 99.99966%.
One of the main pillars of Six Sigma is:
- Customer Centeredness: Every improvement project starts with understanding the customer’s needs and what constitutes “quality” to them.
- Data-driven: Decisions and improvements are based on rigorous quantitative and statistical analysis.
- Systematic improvement (DMAIC): A specific methodology that follows five stages:
Define: Define the issue and goals.
Measure: Measure current performance.
Analyze: Analyze the causes of issues.
Improve: Implement effective solutions.
Control: Stabilize results and prevent regression.
- Build internal competencies: Organization employees are trained at different levels of expertise, such as yellow, green, and black belts, depending on the depth of their involvement in the methodology.
Benefits of Six Sigma
- Minimize waste and losses.
- Significantly improve customer satisfaction.
- Increase process efficiency and productivity.
- Support decision-making based on accurate data rather than intuition.
The idea of Six Sigma is that if an organization is able to measure the number of defects in a process, it can scientifically eliminate those defects and move closer to a defect-free point.
It is very important to understand that each stage of quality system development did not cancel what came before it, but rather included and developed on it.
How Artificial Intelligence (AI) affects the application of the Quality Management System
With the rapid progress in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, it has an important role in the application of quality systems within modern organizations. This is because AI effectively contributes to the accuracy of processes, analyzing data faster, and predicting issues before they occur.
Smart systems can monitor production lines in real time and automatically identify defects without human intervention. It can also be used to analyze customer satisfaction trends and recommend customized improvements to products or services.
Moreover, AI can be integrated into quality management systems (QMS) to provide predictive reports and decision-making support based on performance indicators, which contributes to achieving sustainable quality and continuous improvement with unprecedented accuracy and effectiveness.
Implementing the Stages of a Quality System in Egypt and Saudi Arabia
The two countries seek to implement the quality system in various fields and sectors within Vision 2030 to achieve efficiency, improve services, and enhance regional and international competitiveness. Implementing the Stages of a Quality System in Egypt and Saudi Arabia is a strategic step to ensure the provision of products and services that are in line with international standards and meet the aspirations of citizens and investors.
In Egypt:
Egypt is working to integrate the principles of quality management in state institutions and the private sector, especially in light of the trend towards digital transformation. Some of the most prominent aspects of the application are:
- Adopting ISO 9001 standards in a large number of factories and government agencies.
- Developing the health and educational services system to be in line with international quality standards.
- Spreading the culture of quality within institutions through training and qualification programs.
- Incorporating quality as a key element in the development strategy of the state’s administrative apparatus.
In Saudi Arabia:
It aims to develop the performance of government agencies and improve the quality of life. The main steps of implementation include
- Adopting total quality management (TQM) concepts in government organizations.
- Requiring many vital sectors (health, industry, education) to obtain international quality accreditation certificates.
- Launching programs and initiatives such as “Government Institutional Excellence” and “Academic Institutional Accreditation”.
- Supporting national companies and institutions in applying the latest quality systems to improve performance and reduce costs.
Through knowledge of the stages of quality system development, it is clear that quality has never been a mere technical procedure; on the contrary, adopting modern quality systems is no longer a luxury, but a strategic choice to build flexible organizations capable of competing and achieving customer satisfaction in a rapidly changing environment. A renewed mindset and organizational culture that deepens over time.
It started from manual inspection and progressed through the concepts of quality control and quality assurance, until it reached advanced systems such as TQM and Six Sigma, and today quality is integrated with digital transformation and artificial intelligence.
The quality you establish today is your sustainable success tomorrow.”At Eamak, with a group of experts, we help you implement the latest quality system